Statevector#
- class qiskit.quantum_info.Statevector(data, dims=None)[ソース]#
ベースクラス:
QuantumState,TolerancesMixinStatevector class
Initialize a statevector object.
- パラメータ:
or (data (np.array or list or Statevector or Operator or QuantumCircuit) – qiskit.circuit.Instruction): Data from which the statevector can be constructed. This can be either a complex vector, another statevector, a
Operatorwith only one column or aQuantumCircuitorInstruction. If the data is a circuit or instruction, the statevector is constructed by assuming that all qubits are initialized to the zero state.dims (int or tuple or list) – Optional. The subsystem dimension of the state (See additional information).
- 例外:
QiskitError – if input data is not valid.
- Additional Information:
The
dimskwarg can be None, an integer, or an iterable of integers.Iterable– the subsystem dimensions are the values in the list with the total number of subsystems given by the length of the list.IntorNone– the length of the input vector specifies the total dimension of the density matrix. If it is a power of two the state will be initialized as an N-qubit state. If it is not a power of two the state will have a single d-dimensional subsystem.
Attributes
- atol = 1e-08#
- data#
Return data.
- dim#
Return total state dimension.
- num_qubits#
Return the number of qubits if a N-qubit state or None otherwise.
- rtol = 1e-05#
- settings#
Return settings.
Methods
- copy()#
Make a copy of current operator.
- dims(qargs=None)#
Return tuple of input dimension for specified subsystems.
- draw(output=None, **drawer_args)[ソース]#
Return a visualization of the Statevector.
repr: ASCII TextMatrix of the state’s
__repr__.text: ASCII TextMatrix that can be printed in the console.
latex: An IPython Latex object for displaying in Jupyter Notebooks.
latex_source: Raw, uncompiled ASCII source to generate array using LaTeX.
qsphere: Matplotlib figure, rendering of statevector using plot_state_qsphere().
hinton: Matplotlib figure, rendering of statevector using plot_state_hinton().
bloch: Matplotlib figure, rendering of statevector using plot_bloch_multivector().
city: Matplotlib figure, rendering of statevector using plot_state_city().
paulivec: Matplotlib figure, rendering of statevector using plot_state_paulivec().
- パラメータ:
output (str) – Select the output method to use for drawing the state. Valid choices are repr, text, latex, latex_source, qsphere, hinton, bloch, city, or paulivec. Default is repr. Default can be changed by adding the line
state_drawer = <default>to~/.qiskit/settings.confunder[default].drawer_args – Arguments to be passed directly to the relevant drawing function or constructor (TextMatrix(), array_to_latex(), plot_state_qsphere(), plot_state_hinton() or plot_bloch_multivector()). See the relevant function under qiskit.visualization for that function’s documentation.
- 戻り値:
matplotlib.FigureorstrorTextMatrixorIPython.display.Latex: Drawing of the Statevector.- 例外:
ValueError – when an invalid output method is selected.
サンプル
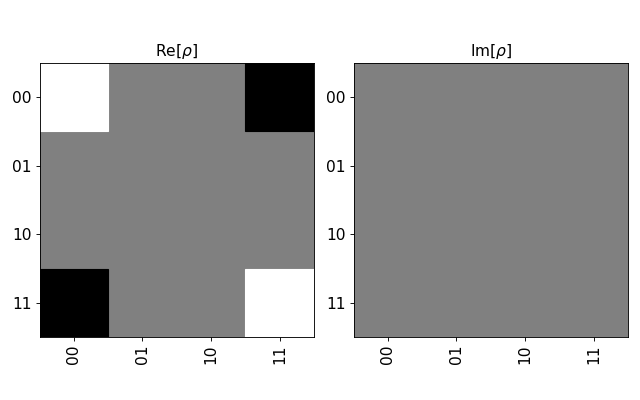
Plot one of the Bell states
from numpy import sqrt from qiskit.quantum_info import Statevector sv=Statevector([1/sqrt(2), 0, 0, -1/sqrt(2)]) sv.draw(output='hinton')
- equiv(other, rtol=None, atol=None)[ソース]#
Return True if other is equivalent as a statevector up to global phase.
注釈
If other is not a Statevector, but can be used to initialize a statevector object, this will check that Statevector(other) is equivalent to the current statevector up to global phase.
- パラメータ:
other (Statevector) – an object from which a
Statevectorcan be constructed.rtol (float) – relative tolerance value for comparison.
atol (float) – absolute tolerance value for comparison.
- 戻り値:
True if statevectors are equivalent up to global phase.
- 戻り値の型:
- evolve(other, qargs=None)[ソース]#
Evolve a quantum state by the operator.
- パラメータ:
other (Operator | QuantumCircuit | circuit.Instruction) – The operator to evolve by.
qargs (list) – a list of Statevector subsystem positions to apply the operator on.
- 戻り値:
the output quantum state.
- 戻り値の型:
- 例外:
QiskitError – if the operator dimension does not match the specified Statevector subsystem dimensions.
- expand(other)[ソース]#
Return the tensor product state other ⊗ self.
- パラメータ:
other (Statevector) – a quantum state object.
- 戻り値:
the tensor product state other ⊗ self.
- 戻り値の型:
- 例外:
QiskitError – if other is not a quantum state.
- classmethod from_instruction(instruction)[ソース]#
Return the output statevector of an instruction.
The statevector is initialized in the state \(|{0,\ldots,0}\rangle\) of the same number of qubits as the input instruction or circuit, evolved by the input instruction, and the output statevector returned.
- パラメータ:
instruction (qiskit.circuit.Instruction or QuantumCircuit) – instruction or circuit
- 戻り値:
The final statevector.
- 戻り値の型:
- 例外:
QiskitError – if the instruction contains invalid instructions for the statevector simulation.
- static from_int(i, dims)[ソース]#
Return a computational basis statevector.
- パラメータ:
- 戻り値:
The computational basis state \(|i\rangle\).
- 戻り値の型:
- Additional Information:
The
dimskwarg can be an integer or an iterable of integers.Iterable– the subsystem dimensions are the values in the list with the total number of subsystems given by the length of the list.Int– the integer specifies the total dimension of the state. If it is a power of two the state will be initialized as an N-qubit state. If it is not a power of two the state will have a single d-dimensional subsystem.
- classmethod from_label(label)[ソース]#
Return a tensor product of Pauli X,Y,Z eigenstates.
Table 12 Single-qubit state labels# Label
Statevector
"0"\([1, 0]\)
"1"\([0, 1]\)
"+"\([1 / \sqrt{2}, 1 / \sqrt{2}]\)
"-"\([1 / \sqrt{2}, -1 / \sqrt{2}]\)
"r"\([1 / \sqrt{2}, i / \sqrt{2}]\)
"l"\([1 / \sqrt{2}, -i / \sqrt{2}]\)
- パラメータ:
label (string) – a eigenstate string ket label (see table for allowed values).
- 戻り値:
The N-qubit basis state density matrix.
- 戻り値の型:
- 例外:
QiskitError – if the label contains invalid characters, or the length of the label is larger than an explicitly specified num_qubits.
- inner(other)[ソース]#
Return the inner product of self and other as \(\langle self| other \rangle\).
- パラメータ:
other (Statevector) – a quantum state object.
- 戻り値:
the inner product of self and other, \(\langle self| other \rangle\).
- 戻り値の型:
np.complex128
- 例外:
QiskitError – if other is not a quantum state or has different dimension.
- measure(qargs=None)#
Measure subsystems and return outcome and post-measure state.
Note that this function uses the QuantumStates internal random number generator for sampling the measurement outcome. The RNG seed can be set using the
seed()method.- パラメータ:
qargs (list or None) – subsystems to sample measurements for, if None sample measurement of all subsystems (Default: None).
- 戻り値:
- the pair
(outcome, state)whereoutcomeis the measurement outcome string label, and
stateis the collapsed post-measurement state for the corresponding outcome.
- the pair
- 戻り値の型:
- probabilities(qargs=None, decimals=None)[ソース]#
Return the subsystem measurement probability vector.
Measurement probabilities are with respect to measurement in the computation (diagonal) basis.
- パラメータ:
- 戻り値:
The Numpy vector array of probabilities.
- 戻り値の型:
np.array
サンプル
Consider a 2-qubit product state \(|\psi\rangle=|+\rangle\otimes|0\rangle\).
from qiskit.quantum_info import Statevector psi = Statevector.from_label('+0') # Probabilities for measuring both qubits probs = psi.probabilities() print('probs: {}'.format(probs)) # Probabilities for measuring only qubit-0 probs_qubit_0 = psi.probabilities([0]) print('Qubit-0 probs: {}'.format(probs_qubit_0)) # Probabilities for measuring only qubit-1 probs_qubit_1 = psi.probabilities([1]) print('Qubit-1 probs: {}'.format(probs_qubit_1))
probs: [0.5 0. 0.5 0. ] Qubit-0 probs: [1. 0.] Qubit-1 probs: [0.5 0.5]
We can also permute the order of qubits in the
qargslist to change the qubit position in the probabilities outputfrom qiskit.quantum_info import Statevector psi = Statevector.from_label('+0') # Probabilities for measuring both qubits probs = psi.probabilities([0, 1]) print('probs: {}'.format(probs)) # Probabilities for measuring both qubits # but swapping qubits 0 and 1 in output probs_swapped = psi.probabilities([1, 0]) print('Swapped probs: {}'.format(probs_swapped))
probs: [0.5 0. 0.5 0. ] Swapped probs: [0.5 0.5 0. 0. ]
- probabilities_dict(qargs=None, decimals=None)#
Return the subsystem measurement probability dictionary.
Measurement probabilities are with respect to measurement in the computation (diagonal) basis.
This dictionary representation uses a Ket-like notation where the dictionary keys are qudit strings for the subsystem basis vectors. If any subsystem has a dimension greater than 10 comma delimiters are inserted between integers so that subsystems can be distinguished.
- パラメータ:
- 戻り値:
The measurement probabilities in dict (ket) form.
- 戻り値の型:
- reset(qargs=None)[ソース]#
Reset state or subsystems to the 0-state.
- パラメータ:
qargs (list or None) – subsystems to reset, if None all subsystems will be reset to their 0-state (Default: None).
- 戻り値:
the reset state.
- 戻り値の型:
- Additional Information:
If all subsystems are reset this will return the ground state on all subsystems. If only a some subsystems are reset this function will perform a measurement on those subsystems and evolve the subsystems so that the collapsed post-measurement states are rotated to the 0-state. The RNG seed for this sampling can be set using the
seed()method.
- reverse_qargs()[ソース]#
Return a Statevector with reversed subsystem ordering.
For a tensor product state this is equivalent to reversing the order of tensor product subsystems. For a statevector \(|\psi \rangle = |\psi_{n-1} \rangle \otimes ... \otimes |\psi_0 \rangle\) the returned statevector will be \(|\psi_{0} \rangle \otimes ... \otimes |\psi_{n-1} \rangle\).
- 戻り値:
the Statevector with reversed subsystem order.
- 戻り値の型:
- sample_counts(shots, qargs=None)#
Sample a dict of qubit measurement outcomes in the computational basis.
- パラメータ:
- 戻り値:
sampled counts dictionary.
- 戻り値の型:
Additional Information:
This function samples measurement outcomes using the measure
probabilities()for the current state and qargs. It does not actually implement the measurement so the current state is not modified.The seed for random number generator used for sampling can be set to a fixed value by using the stats
seed()method.
- sample_memory(shots, qargs=None)#
Sample a list of qubit measurement outcomes in the computational basis.
- パラメータ:
- 戻り値:
list of sampled counts if the order sampled.
- 戻り値の型:
np.array
Additional Information:
This function samples measurement outcomes using the measure
probabilities()for the current state and qargs. It does not actually implement the measurement so the current state is not modified.The seed for random number generator used for sampling can be set to a fixed value by using the stats
seed()method.
- seed(value=None)#
Set the seed for the quantum state RNG.
- tensor(other)[ソース]#
Return the tensor product state self ⊗ other.
- パラメータ:
other (Statevector) – a quantum state object.
- 戻り値:
the tensor product operator self ⊗ other.
- 戻り値の型:
- 例外:
QiskitError – if other is not a quantum state.
- to_dict(decimals=None)[ソース]#
Convert the statevector to dictionary form.
This dictionary representation uses a Ket-like notation where the dictionary keys are qudit strings for the subsystem basis vectors. If any subsystem has a dimension greater than 10 comma delimiters are inserted between integers so that subsystems can be distinguished.
- パラメータ:
decimals (None or int) – the number of decimal places to round values. If None no rounding is done (Default: None).
- 戻り値:
the dictionary form of the Statevector.
- 戻り値の型:
サンプル
The ket-form of a 2-qubit statevector \(|\psi\rangle = |-\rangle\otimes |0\rangle\)
from qiskit.quantum_info import Statevector psi = Statevector.from_label('-0') print(psi.to_dict())
{'00': (0.7071067811865475+0j), '10': (-0.7071067811865475+0j)}
For non-qubit subsystems the integer range can go from 0 to 9. For example in a qutrit system
import numpy as np from qiskit.quantum_info import Statevector vec = np.zeros(9) vec[0] = 1 / np.sqrt(2) vec[-1] = 1 / np.sqrt(2) psi = Statevector(vec, dims=(3, 3)) print(psi.to_dict())
{'00': (0.7071067811865475+0j), '22': (0.7071067811865475+0j)}
For large subsystem dimensions delimiters are required. The following example is for a 20-dimensional system consisting of a qubit and 10-dimensional qudit.
import numpy as np from qiskit.quantum_info import Statevector vec = np.zeros(2 * 10) vec[0] = 1 / np.sqrt(2) vec[-1] = 1 / np.sqrt(2) psi = Statevector(vec, dims=(2, 10)) print(psi.to_dict())
{'00': (0.7071067811865475+0j), '91': (0.7071067811865475+0j)}