ControlledGate¶
- class qiskit.circuit.ControlledGate(name, num_qubits, params, label=None, num_ctrl_qubits=1, definition=None, ctrl_state=None, base_gate=None, duration=None, unit=None, *, _base_label=None)[source]¶
Bases:
GateControlled unitary gate.
Create a new ControlledGate. In the new gate the first
num_ctrl_qubitsof the gate are the controls.- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the gate.
num_qubits (int) – The number of qubits the gate acts on.
params (list) – A list of parameters for the gate.
label (Optional[str]) – An optional label for the gate.
num_ctrl_qubits (Optional[int]) – Number of control qubits.
definition (Optional['QuantumCircuit']) – A list of gate rules for implementing this gate. The elements of the list are tuples of (
Gate(), [qubit_list], [clbit_list]).ctrl_state (Optional[Union[int, str]]) – The control state in decimal or as a bitstring (e.g. ‘111’). If specified as a bitstring the length must equal num_ctrl_qubits, MSB on left. If None, use 2**num_ctrl_qubits-1.
base_gate (Optional[Gate]) – Gate object to be controlled.
- Raises:
CircuitError – If
num_ctrl_qubits>=num_qubits.CircuitError – ctrl_state < 0 or ctrl_state > 2**num_ctrl_qubits.
Examples:
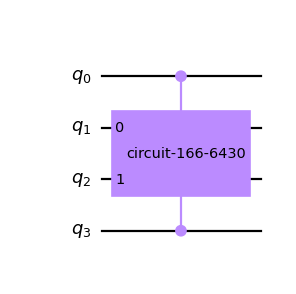
Create a controlled standard gate and apply it to a circuit.
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit, QuantumRegister from qiskit.circuit.library.standard_gates import HGate qr = QuantumRegister(3) qc = QuantumCircuit(qr) c3h_gate = HGate().control(2) qc.append(c3h_gate, qr) qc.draw('mpl')
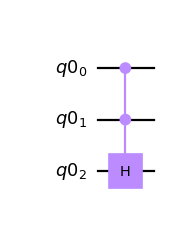
Create a controlled custom gate and apply it to a circuit.
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit, QuantumRegister from qiskit.circuit.library.standard_gates import HGate qc1 = QuantumCircuit(2) qc1.x(0) qc1.h(1) custom = qc1.to_gate().control(2) qc2 = QuantumCircuit(4) qc2.append(custom, [0, 3, 1, 2]) qc2.draw('mpl')
Attributes
- base_class¶
Get the base class of this instruction. This is guaranteed to be in the inheritance tree of
self.The “base class” of an instruction is the lowest class in its inheritance tree that the object should be considered entirely compatible with for _all_ circuit applications. This typically means that the subclass is defined purely to offer some sort of programmer convenience over the base class, and the base class is the “true” class for a behavioural perspective. In particular, you should not override
base_classif you are defining a custom version of an instruction that will be implemented differently by hardware, such as an alternative measurement strategy, or a version of a parametrised gate with a particular set of parameters for the purposes of distinguishing it in aTargetfrom the full parametrised gate.This is often exactly equivalent to
type(obj), except in the case of singleton instances of standard-library instructions. These singleton instances are special subclasses of their base class, and this property will return that base. For example:>>> isinstance(XGate(), XGate) True >>> type(XGate()) is XGate False >>> XGate().base_class is XGate True
In general, you should not rely on the precise class of an instruction; within a given circuit, it is expected that
Instruction.nameshould be a more suitable discriminator in most situations.
- condition¶
The classical condition on the instruction.
- condition_bits¶
Get Clbits in condition.
- ctrl_state¶
Return the control state of the gate as a decimal integer.
- decompositions¶
Get the decompositions of the instruction from the SessionEquivalenceLibrary.
- definition¶
Return definition in terms of other basic gates. If the gate has open controls, as determined from self.ctrl_state, the returned definition is conjugated with X without changing the internal _definition.
- duration¶
Get the duration.
- label¶
Return instruction label
- mutable¶
Is this instance is a mutable unique instance or not.
If this attribute is
Falsethe gate instance is a shared singleton and is not mutable.
- name¶
Get name of gate. If the gate has open controls the gate name will become:
<original_name_o<ctrl_state>
where <original_name> is the gate name for the default case of closed control qubits and <ctrl_state> is the integer value of the control state for the gate.
- num_clbits¶
Return the number of clbits.
- num_ctrl_qubits¶
Get number of control qubits.
- Returns:
The number of control qubits for the gate.
- Return type:
- num_qubits¶
Return the number of qubits.
- params¶
Get parameters from base_gate.
- Returns:
List of gate parameters.
- Return type:
- Raises:
CircuitError – Controlled gate does not define a base gate
- unit¶
Get the time unit of duration.
Methods
- add_decomposition(decomposition)¶
Add a decomposition of the instruction to the SessionEquivalenceLibrary.
- assemble()¶
Assemble a QasmQobjInstruction
- broadcast_arguments(qargs, cargs)¶
Validation and handling of the arguments and its relationship.
For example,
cx([q[0],q[1]], q[2])meanscx(q[0], q[2]); cx(q[1], q[2]). This method yields the arguments in the right grouping. In the given example:in: [[q[0],q[1]], q[2]],[] outs: [q[0], q[2]], [] [q[1], q[2]], []
The general broadcasting rules are:
If len(qargs) == 1:
[q[0], q[1]] -> [q[0]],[q[1]]
If len(qargs) == 2:
[[q[0], q[1]], [r[0], r[1]]] -> [q[0], r[0]], [q[1], r[1]] [[q[0]], [r[0], r[1]]] -> [q[0], r[0]], [q[0], r[1]] [[q[0], q[1]], [r[0]]] -> [q[0], r[0]], [q[1], r[0]]
If len(qargs) >= 3:
[q[0], q[1]], [r[0], r[1]], ...] -> [q[0], r[0], ...], [q[1], r[1], ...]
- Parameters:
- Returns:
A tuple with single arguments.
- Raises:
CircuitError – If the input is not valid. For example, the number of arguments does not match the gate expectation.
- Return type:
- c_if(classical, val)¶
Set a classical equality condition on this instruction between the register or cbit
classicaland valueval.Note
This is a setter method, not an additive one. Calling this multiple times will silently override any previously set condition; it does not stack.
- control(num_ctrl_qubits=1, label=None, ctrl_state=None)¶
Return controlled version of gate. See
ControlledGatefor usage.- Parameters:
- Returns:
Controlled version of gate. This default algorithm uses
num_ctrl_qubits-1ancilla qubits so returns a gate of sizenum_qubits + 2*num_ctrl_qubits - 1.- Return type:
- Raises:
QiskitError – unrecognized mode or invalid ctrl_state
- copy(name=None)¶
Copy of the instruction.
- Parameters:
name (str) – name to be given to the copied circuit, if
Nonethen the name stays the same.- Returns:
a copy of the current instruction, with the name updated if it was provided
- Return type:
- is_parameterized()¶
Return True .IFF. instruction is parameterized else False
- power(exponent)¶
Creates a unitary gate as gate^exponent.
- Parameters:
exponent (float) – Gate^exponent
- Returns:
To which to_matrix is self.to_matrix^exponent.
- Return type:
.library.UnitaryGate
- Raises:
CircuitError – If Gate is not unitary
- qasm()¶
Return a default OpenQASM string for the instruction.
Derived instructions may override this to print in a different format (e.g.
measure q[0] -> c[0];).Deprecated since version 0.25.0: The method
qiskit.circuit.instruction.Instruction.qasm()is deprecated as of qiskit-terra 0.25.0. It will be removed no earlier than 3 months after the release date. Correct exporting to OpenQASM 2 is the responsibility of a larger exporter; it cannot safely be done on an object-by-object basis without context. No replacement will be provided, because the premise is wrong.
- repeat(n)¶
Creates an instruction with gate repeated n amount of times.
- Parameters:
n (int) – Number of times to repeat the instruction
- Returns:
Containing the definition.
- Return type:
- Raises:
CircuitError – If n < 1.
- reverse_ops()¶
For a composite instruction, reverse the order of sub-instructions.
This is done by recursively reversing all sub-instructions. It does not invert any gate.
- Returns:
- a new instruction with
sub-instructions reversed.
- Return type:
- soft_compare(other)¶
Soft comparison between gates. Their names, number of qubits, and classical bit numbers must match. The number of parameters must match. Each parameter is compared. If one is a ParameterExpression then it is not taken into account.
- Parameters:
other (instruction) – other instruction.
- Returns:
are self and other equal up to parameter expressions.
- Return type:
- to_matrix()¶
Return a Numpy.array for the gate unitary matrix.
- Returns:
if the Gate subclass has a matrix definition.
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- Raises:
CircuitError – If a Gate subclass does not implement this method an exception will be raised when this base class method is called.
- to_mutable()¶
Return a mutable copy of this gate.
This method will return a new mutable copy of this gate instance. If a singleton instance is being used this will be a new unique instance that can be mutated. If the instance is already mutable it will be a deepcopy of that instance.
- validate_parameter(parameter)¶
Gate parameters should be int, float, or ParameterExpression